How To Build Agriculture Software: A Detailed Guide

Table of Contents
Introduction
Agriculture stands as the backbone of civilization, providing sustenance, economic stability, and environmental balance for centuries. As the global population continues to grow, the demand for food and agricultural products escalates, presenting both challenges and opportunities for the industry. In response, technology emerges as a critical ally, offering innovative solutions to enhance productivity and efficiency. At the forefront of this technological revolution lies agriculture software development, poised to revolutionize traditional farming practices.
In this guide, we’ll delve into the world of agriculture software, exploring its significance, functionality, and the steps involved in its development, paving the way for a future where technology and agriculture converge for the greater good.
What is Agriculture Software Development?
Agriculture software development involves creating digital solutions tailored to aid farmers in managing their operations efficiently. These software applications, platforms, and tools are designed to automate various farming processes such as planting, irrigation, and harvesting. By harnessing technology, agriculture software provides valuable insights through data analysis, enabling farmers to make informed decisions and optimize their practices.
How Agriculture Software Works
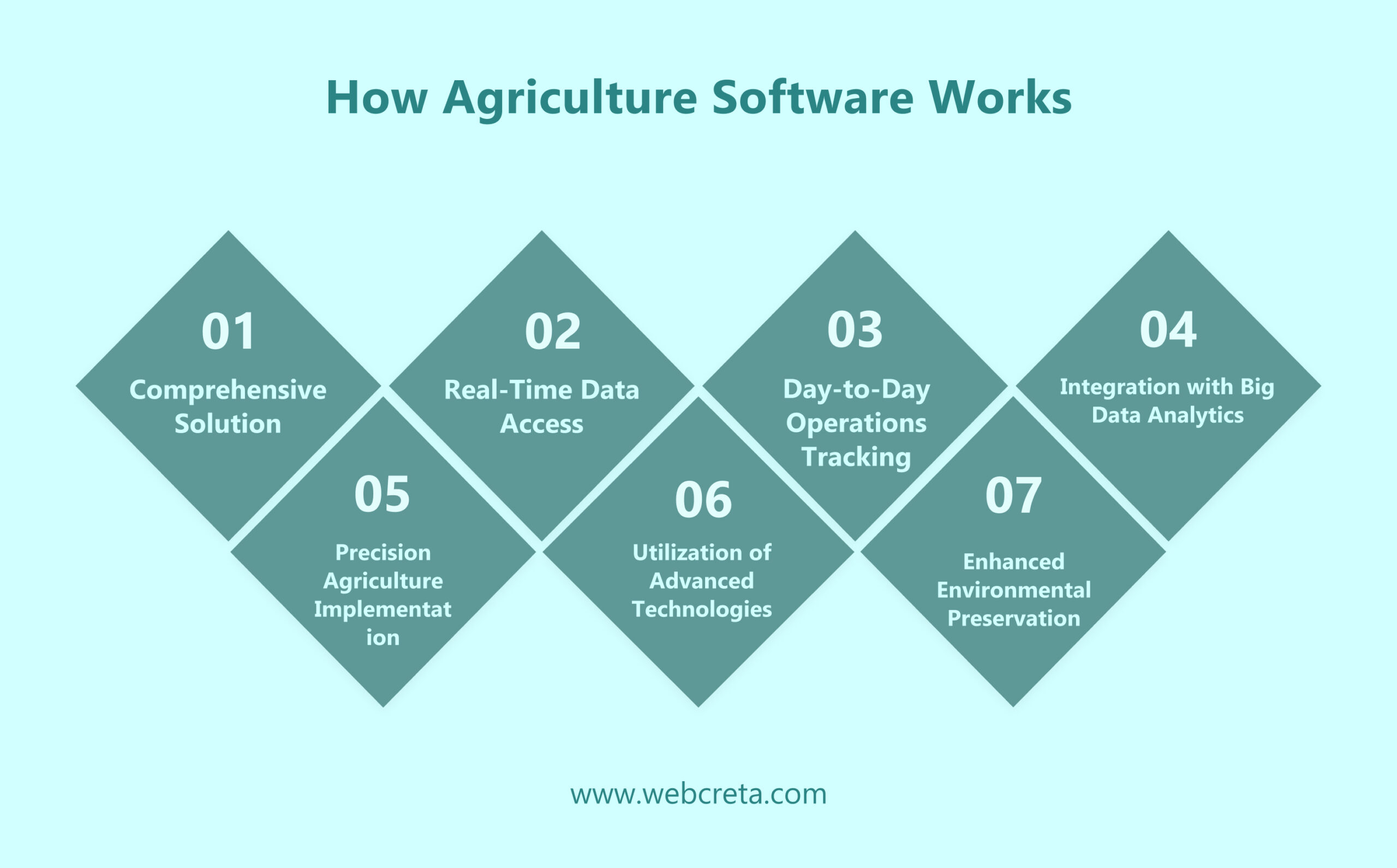
1) Comprehensive Solution:
Agriculture software serves as a comprehensive solution for farm management, enabling farmers to track crop planning, livestock management, pest control, record-keeping, and risk management efficiently.
2) Real-Time Data Access:
Farmers can access real-time data through agriculture software, allowing them to monitor their performance, understand farm equipment and labor management, and make data-driven decisions promptly.
3) Day-to-Day Operations Tracking:
Agri software enables tracking and analysis of day-to-day farm operations, improving production efficiency and profitability. It includes features like crop management, worker progress tracking, and collaboration tools.
4) Integration with Big Data Analytics:
The software integrates with big data analytics to provide valuable insights for farmers. It helps in making better decisions, optimizing resource usage like water, fertilizer, and pesticides, and improving crop yield.
5) Precision Agriculture Implementation:
Precision agriculture software ensures that soil and crops receive the exact nutrients they need for optimal health and yield. It considers factors like soil type, geography, weather conditions, plant growth data, and yield information for sustainable farming practices.
6) Utilization of Advanced Technologies:
Precision agriculture software utilizes technologies like drones for assessment, GIS tools for land data analysis, IoT devices for field data collection, machine learning algorithms for recommendations, and predictive analytics for forecasting.
7) Enhanced Environmental Preservation:
Precision agriculture software not only improves profitability but also ensures sustainability and environmental preservation by optimizing resource usage like water and fertilizers. It helps in preventing soil deterioration and improving water use efficiency.
Types of Agriculture Software
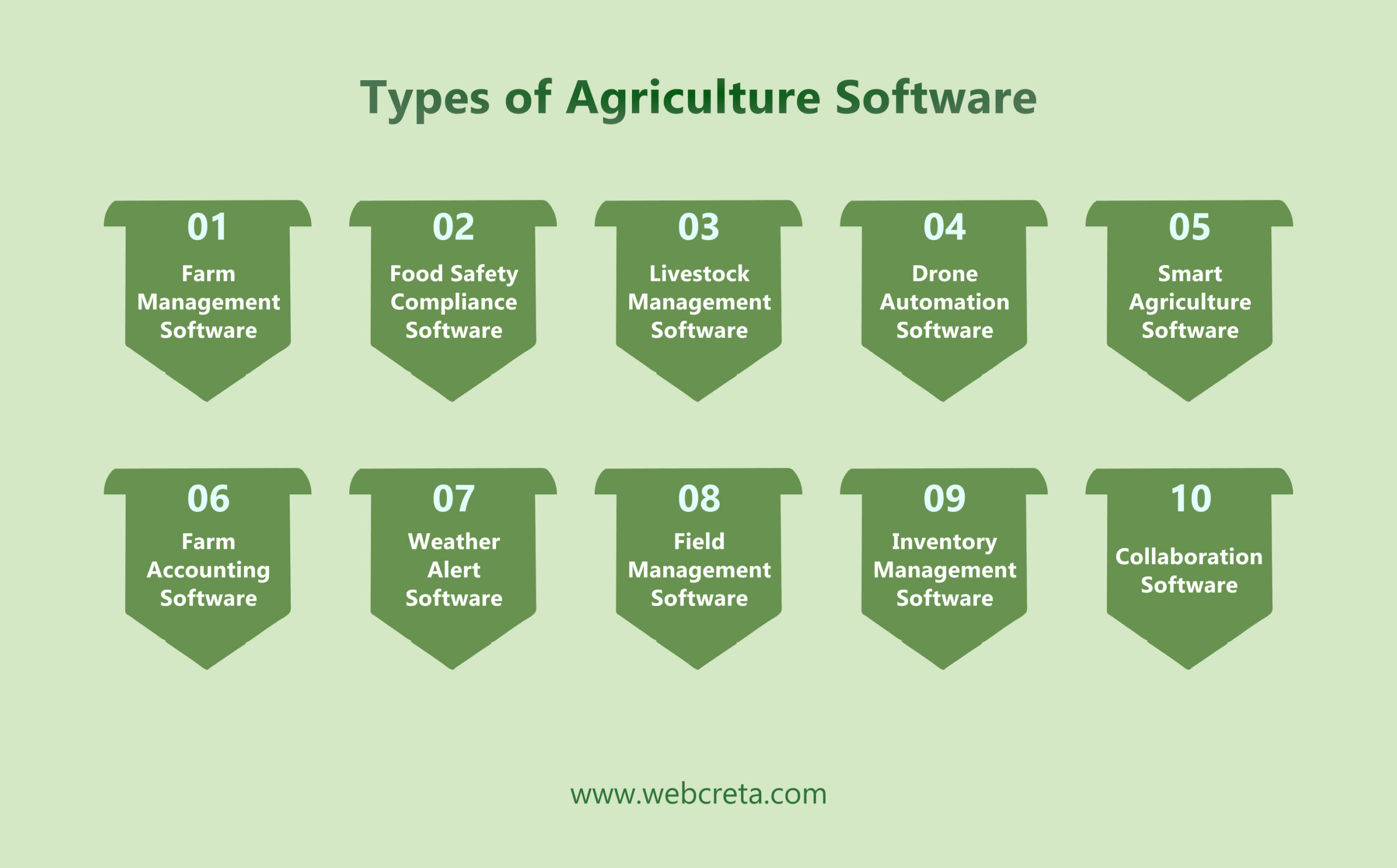
1) Farm Management Software:
This type of software helps farmers streamline their operations by providing tools for planning, monitoring, and analyzing various aspects of their farm. It covers activities such as crop management, inventory tracking, financial management, and labor management.
2) Food Safety Compliance Software:
Food safety compliance software focuses on ensuring that farmers adhere to strict food safety regulations and standards. It helps in maintaining traceability, quality control, and compliance with industry requirements to ensure the production of safe and high-quality agricultural products.
3) Livestock Management Software:
Livestock management software is designed to assist farmers in managing their livestock effectively. It includes features for tracking animal health, growth, breeding, and overall well-being. This software helps farmers optimize their livestock operations and ensure the health and productivity of their animals.
4) Drone Automation Software:
Drone automation software leverages drone technology to automate tasks such as crop monitoring, spraying pesticides, fertilizing, and conducting aerial surveys. By using drones, farmers can gather valuable data, improve efficiency, and make informed decisions to enhance their farming practices.
5) Smart Agriculture Software:
Smart agriculture software integrates advanced technologies like smart sensors, Internet of Things (IoT) devices, and data analytics to optimize farming processes. It enables farmers to monitor and manage their resources more efficiently, improve crop yields, and promote sustainable agricultural practices.
6) Farm Accounting Software:
Farm accounting software is essential for financial management on the farm. It helps farmers track expenses, profits, inventory, and overall financial performance. By providing insights into financial data, this software enables farmers to make informed decisions to optimize their financial resources.
7) Weather Alert Software:
Weather alert software provides real-time weather forecasts and alerts to farmers. By staying informed about weather conditions, farmers can plan and adjust their farming activities accordingly. This software helps farmers mitigate risks associated with adverse weather and optimize their farming operations.
8) Field Management Software:
Field management software assists farmers in managing their fields effectively. It includes features for monitoring crop rotation, irrigation scheduling, soil health, and resource allocation. This software helps farmers optimize field operations and maximize productivity.
9) Inventory Management Software:
Inventory management software helps farmers track and manage their inventory efficiently. It ensures accurate stock levels, prevents overstocking or shortages, and enables farmers to optimize their inventory management processes.
10) Collaboration Software:
Collaboration software fosters communication and collaboration among farmers. It provides a platform for sharing ideas, best practices, and insights within the farming community. By promoting collaboration, this software helps farmers learn from each other, improve productivity, and drive innovation in agriculture.
Benefits of Agri Software Development
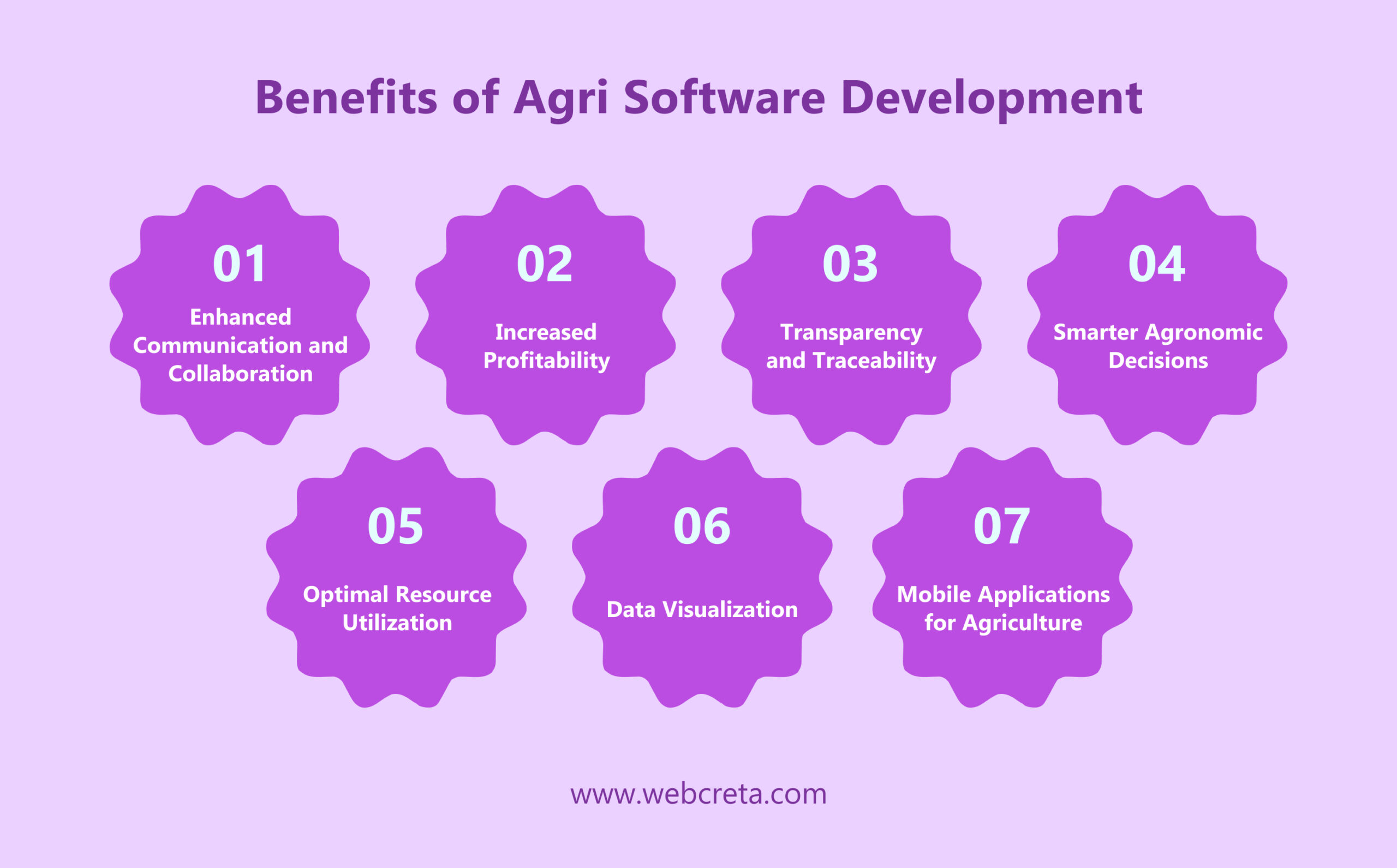
1) Enhanced Communication and Collaboration:
Agri software development facilitates communication and collaboration among workers, enabling efficient monitoring and management of their development processes.
2) Increased Profitability:
Users of farm crop management software can benefit from increased profitability by tracking manufacturing expenses, crew working hours, and accessing real-time data for profitable decision-making.
3) Transparency and Traceability:
Good farm crop management software provides user-friendly traceability tools for precise tracking of operations, ensuring transparency in processes and quick access to records when needed.
4) Smarter Agronomic Decisions:
Agri software aids farmers in making smarter agronomic decisions by gathering and synthesizing vast amounts of data from various sources like federal agricultural databases, satellite images, soil monitors, and weather stations.
5) Optimal Resource Utilization:
Precision agriculture software helps farmers maximize crop yield while minimizing waste through informed decisions on inputs like water, fertilizer, and materials. This leads to increased crop yields, lower input costs, and enhanced environmental sustainability.
6) Data Visualization:
Agricultural software utilizes big data to visualize information into easy-to-understand charts and graphs. This aids farmers in gaining insights into their fields quickly without sorting through large volumes of raw data.
7) Mobile Applications for Agriculture:
The development of mobile apps for agriculture allows farmers to monitor weather patterns, soil quality, crop health, equipment maintenance, inventories, and supply chain logistics efficiently. These apps enhance productivity and efficiency on the farm.
Steps by Steps Guide to Develop Agriculture Software
1) Vision and Idea:
The initial step in developing agriculture software involves defining the vision and idea behind the software. This includes identifying the purpose, target audience, and unique selling points of the software.
2) Technical Specifications and Business Analysis:
The next stage involves technical specialists translating the concepts into a set of capabilities through technical specifications and business analysis. This step ensures that every aspect of the development process is considered, including cost, timeline, and resources.
3) Pre-Development Stage:
This phase focuses on planning the entire project, including developing APIs, backend systems, cloud storage solutions, and software design. Careful planning is crucial for complex software projects to ensure a smooth development process.
4) Development and Testing:
The actual development of agriculture software begins at this stage. Quality control teams test the software feature by feature to identify and address any issues. Testing in real-world conditions is essential for ensuring the software functions as intended.
5) Deployment:
Once the software has been thoroughly tested and meets all requirements, it is deployed for public use. This phase marks the final step before making the software available to users.
6) Maintenance and Support:
The development process doesn’t end with deployment; ongoing maintenance is crucial to keep the software up-to-date with new frameworks and technological advancements. Regular updates ensure that the software remains current and continues to provide value to users.
Cost Considerations for Agriculture Software Development
The cost of developing agriculture software can vary widely depending on factors like complexity, features, and technologies used. Basic applications may start at $10,000 to $20,000, while more advanced solutions can range from $30,000 to $200,000 or more. Factors influencing the cost include application complexity, size, and the location of developers. The development process involves defining the problem, planning, design, development, testing, and maintenance to ensure the software meets user needs effectively.
Agriculture software development aims to provide valuable insights into farm operations, streamline processes for farmers and agribusinesses, and enhance productivity in the agricultural industry.
Factors to Consider for Agriculture Software Development Costs

1) Scope and Complexity:
The scope and complexity of the agriculture software project significantly impact the development cost. A larger scope with advanced features and functionalities will require more time and resources, thus increasing the overall cost.
2) Use of Third-Party Tools and Open Source Technologies:
Leveraging open source technologies and third-party tools can help reduce costs by utilizing pre-existing code and resources, rather than starting from scratch. This approach can be cost-effective and efficient in software development.
3) Quality and Testing Requirements:
Projects that demand a higher level of quality and extensive testing will generally be more expensive. Ensuring that the software meets desired standards before launch, especially for complex applications, can increase development costs.
4) Size and Location of Development Team:
The size and location of the development team can influence costs. Larger teams may complete work faster but will be more expensive due to additional salaries and overhead costs. Remote teams or teams in different regions can impact communication and costs differently.
5) Experience and Expertise of Development Team:
The experience and expertise of the development team play a crucial role in project costs. Teams with higher expertise may be more expensive but can complete work efficiently with fewer errors, while less experienced teams may be more affordable but could take longer to deliver the project.
6) Future Maintenance and Support:
Considering ongoing maintenance and support requirements is essential in determining the overall cost of agriculture software development. Post-launch tasks like bug fixes, updates, and user support contribute to the total cost of the project.
Conclusion
Agriculture software development is revolutionizing farming practices by providing digital tools that streamline operations, automate tasks, and offer valuable insights for informed decision-making, shaping the future of agriculture.
In this blog, we offer valuable insights into agriculture software development, highlighting the role of technology in optimizing farm operations. To elevate your agricultural endeavours, consider partnering with Webcreta, a trusted software development company known for delivering innovative solutions to enhance productivity and efficiency in the agricultural sector.